Periodontal disease is mainly caused by dental plaque, i.e. micro-organisms that live in it. Dental or tooth plaque is a colorless plaque that over time deposits on the teeth, tongue, and mouth cavity. It can be removed by regular -daily teeth brushing.
Periodontopathy is a progressive and degenerative disease of supportive tissue of teeth (periodontium), resulting in teeth oscillation, migration and teeth loss in the terminal (final) stage. Nowadays, it is an increasingly present disease with very young people, where a limit for the first symptoms came down from the late thirties to the early twenties. According to the latest research, teeth loss is even 50% caused by periodontopathic, while caries is responsible for the second half as a causative agent.
Periodontal disease cannot be cured, only stopped at a certain stage and time slowed. Because of that prevention is the most important and it involves removal of soft and hard plaque, regular teeth brushing, and visits to the dentist every 6 months.
---fb88cca21379e0b6f7e45a77faaff0099646759e.jpg)
Deposition of minerals from saliva in plaque creates tooth tartar.
The tartar has a double effect on the development of periodontal disease:
Symptoms of periodontal disease are:
If gingivitis is not cured, tooth tartar continuous its double role in tissue destruction:
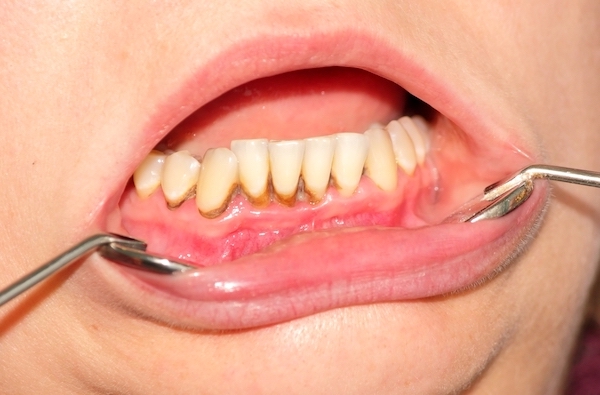
By the destruction of the connecting tissue around the tooth root, the empty space remains - the periodontal pocket. Over time the space deepens and progresses to the top of the tooth root. When total destruction of the tissue occurs as a consequence, there is nothing left to support and connect the tooth in the dental cup-alveolus which leads to the teeth oscillation and loss. The whole process is divided into several clinical stages, therapy is defined according to a certain stage, i.e. to the degree of periodontium destruction.
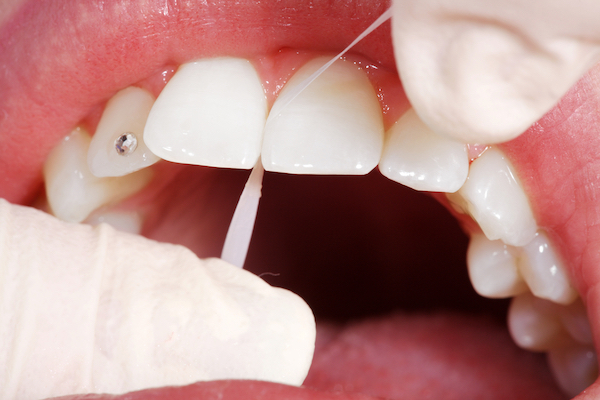
When the depth of the periodontal pocket (which is normally 2mm) is more than 4mm, we suggest surgical treatment, so-called flap surgery. Where pockets are up to 3,4mm maximum depth, persistent and long-term therapy must be carried out . First of all, it means removal of hard and soft deposits in several sessions, raising oral hygiene at the highest level, the use of inter-dental brushes and dental floss with gels for rubbing the gyms as well anti-bacterial solutions for mouthwash. It is necessary to maintain periodontopathic at the same level constantly, i.e. not to allow the disease to progress further on because it cannot be cured. If periodontal pockets are deeper than 4mm, flap surgery is the best solution where it is possible to perform, since in the terminal (final) stage teeth loss is impossible to stop.
